Strengthen Your IP Strategy Today, Secure Tomorrow's Success
Unlock the power of strategic innovation with our comprehensive IP strategy solutions. Don’t wait to protect your brilliant ideas – seize the advantage now and safeguard your future success. Your intellectual property deserves the best defense, and we’re here to make it happen.

Intellectual Property Strategy (IP Strategy) is easy to say, but very hard to do. One of the reasons that make it hard to do is the lack of understanding about what a client means by IP strategy. It’s hard to define before we actually develop it, though we know it when we see it actually in practice. This difficulty in defining its precise meaning is a problem for IP strategists since it is linked to the entire corporate agenda of a company. At Maxinov, IP strategists understand this very well and know how to handle difficult situations associated with a company’s environment.
What does IP strategy broadly mean?
IP strategy (Patent strategy) is a part of overall corporate strategy of a company. One of the main objectives of IP strategy is “sustainable competitive advantage”, which involves a course of actions that will enable your company to generate a sustainable stream of profits.
It is wrong to say that only big firms require IP strategy. In fact, even startups and individual inventors involved in the process of innovation require a patent/IP strategy in order to lay a strong and secured foundation for their business. Whether it is a big corporation or a mid-size firm or a startup or an inventor practicing at an individual level – all need IP strategy. However, IP strategy for each of them will be different.
In short, IP strategy is the development of a course of actions that uses intellectual property to enable a company to sustainably gain competitive advantage by either or more of realizing higher prices, increasing market share, and/or maintaining lower costs than the competition in the long-term with a secured and robust business foundation.
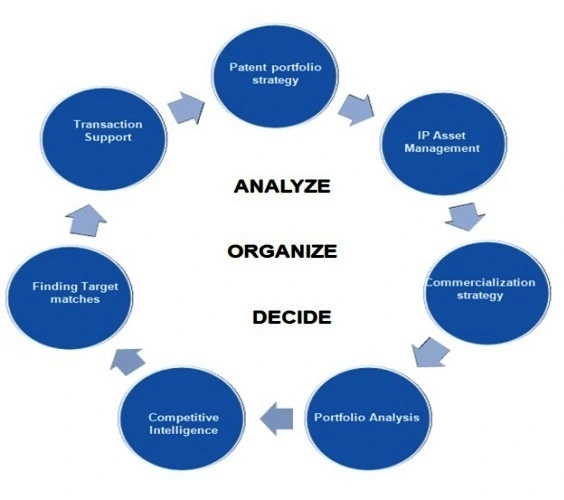
Phases of IP strategy: Find with our team whether and when do you need them
The process of IP strategy in context of patents broadly involves these phases:
Patent portfolio strategy – it ensures alignment between business goals and patent strategy, establishes criteria for guiding invention assessment, identifies gaps to be built via acquisition, etc. Patent portfolio strategy will allow you to understand how to build your patent portfolio to protect core technologies, processes, and business practices uncovered during the audit phase. A patent portfolio is built with a combination of jewel patents, fence patents, and design-around patents.
IP Asset Management – also involves portfolio analysis, can help clients understand where they have gaps in their patent protection by mapping their IP “umbrella” against their key sources of revenue, as well as identifying where they may be spending unnecessarily to support IP no longer core to the business. Taken together, these analyses help a client identify how to protect themselves most cost-effectively.
Commercialization strategy – commercialization strategy support work begins with a detailed assessment of a client’s patent portfolio and where it fits within the relevant technology domain and market space. The portfolio is evaluated in terms of the intrinsic strength of the patents included, as well as the value of its IP to the economics in its marketplace. Together, these steps provide the basis for execution of an effective commercialization effort realizing revenues from IP assets of a company.
Portfolio Analysis – we help organize a client’s patents by creating a taxonomy using patent classification codes or client’s business requirements and analyze each patent within its classification. This taxonomy catalogs and examines patents by technology domains and sub-domains describing key elements of their technology and also evaluates the portfolio’s strength within a defined market.
Competitive Intelligence – it is a thorough analysis of patent assets in a specific technology domain; it highlights major roadblocks to technology or product development and identifies opportunities for R&D and future product development, patenting, licensing, etc. The report evaluates products, people, companies, and best practices and provides insights on competition within a defined market.
Finding Target matches – it involves a thorough Patent/Technology Landscape Analysis to identify potential patent portfolios and/or companies that fit a client’s criteria for acquisition or In-licensing, or collaboration for mutual benefits as well as those that may be infringers of an existing patent or portfolio.
Transaction Support – combines research support for the transaction in consideration including evaluation of patents and market context within which they exist, with guidance regarding transaction structuring issues and market dynamics for key business elements of a company.